This week the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA) released “A Turn Toward Safety: The Safer Intersections Project,” a report detailing the impact of the Left Turn Traffic Calming Project and the “Safety—It’s Your Turn” education campaign. The Safer Intersections Project now has tested traffic interventions that can reduce unsafe left turns. Overall, SFMTA found a 17% reduction in average speed (1.7mph slower) and a 71% reduction in the likelihood of a car turning left at higher speeds over 15mph at seven high-crash test intersections.
In 2019, 40% of traffic deaths in San Francisco were caused when drivers made left turns and didn’t see the person in the crosswalk, until it was too late. To combat this trend, also seen in other cities, and encourage safer left turns and adoption of safer left turn behaviors, San Francisco’s multilayered project combined engineering treatments in seven high-crash intersections with an education campaign, which led to promising results.
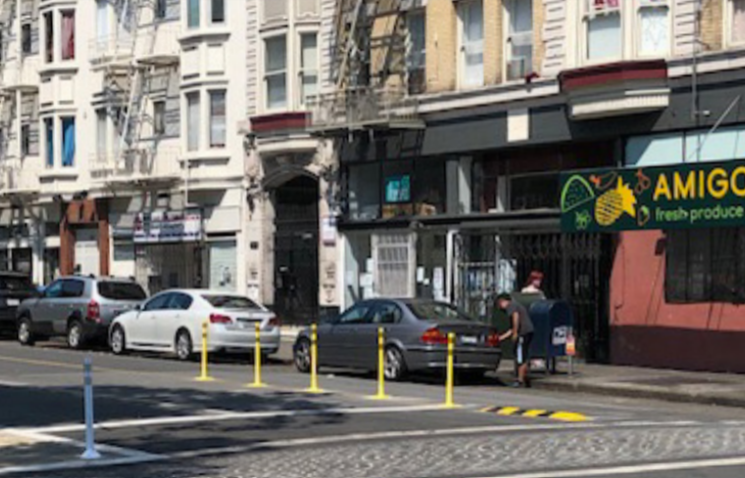
The Left Turn Traffic Calming Project consisted of installing waist-high vertical delineator posts, small rubber speed bumps, and paint to create enhanced center lane lines and painted safety zones to encourage slower, wider left turns and increase drivers’ awareness of other road users. To measure the impact, SFMTA collected left-turning driver speeds before and after installation and then compared driver speeds at the seven project intersections with four other control intersections. The result of this project showed that these treatments are proven to slow driver speeds and encourage safer left turns for both people in the crosswalks and opposing traffic.

The second part of the Safer Intersections Project was designing and implementing an education and community outreach campaign– “Safety—It’s Your Turn” –funded by a $2 million grant through the California Transportation Commission Active Transportation Program. The campaign presented three safer left turn behaviors (Take it slow—5mph is safest; Make it square—90-degree angles are best; and Stay aware—look out for cars, cyclists, and people) and data suggests the “Safety—It’s Your Turn” campaign extended the speed reductions from the Left Turns Traffic Calming project. Year-to-year survey results also show that public perception of the dangers of speeding is trending in the right direction, indicating a sustained change in attitudes influenced by education campaigns and engineering.
A unique aspect of this project was the use of behavioral science. SFMTA partnered with the Behavioral Insights Team (BIT), a leading behavioral science organization, to analyze how drivers make left turns in order to develop interventions that would prompt safer behaviors. By changing the architecture of intersections, we were able to move people toward making safer left turns in the moment. The combination of these physical changes and SFMTA’s educational campaign encouraged safe driving behaviors and increased awareness of how individual actions have an impact on the community.

The education campaign also included working with community-based organizations (CBOs) to broaden and deepen the traffic safety messaging. Through a community grant process, six CBOs were compensated for their time and knowledge, creating additional materials and events supporting the campaign. Many of our grantees were new to Vision Zero and helped us reach additional residents through creative ways such as food delivery, artistic public service announcements, virtual bike rides, and youth poster contests. Finally, we worked with an additional eight CBOs to share educational materials and present the Safety—It’s Your Turn campaign to their members.
In addition to the treatments’ impact on slower speeds, there were two key takeaways from the project:
- Well-funded and evidenced-based education campaigns are an important and effective tool in in raising public awareness, encouraging safer driving behaviors, influencing policy discussions, and building community support.
- For maximum effectiveness, calming treatments should become a standard engineering tool and applied at locations with existing high left-turn speeds, conducive street geometry, and lots of people walking and biking.